Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Example 1:
1
2
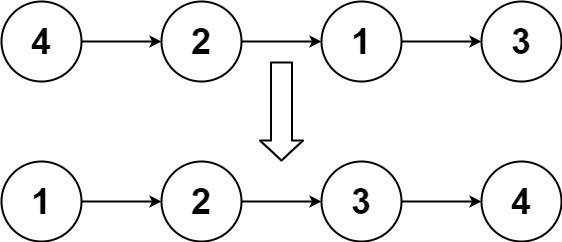
| Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
|
Example 2:

1
2
| Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
|
Example 3:
1
2
| Input: head = []
Output: []
|
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
1 递归
递归方法很简单, 但是不满足空间复杂度O(1)的要求.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null)
{
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode list2 = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode list1 = head;
ListNode sortedList1 = sortList(list1);
ListNode sortedList2 = sortList(list2);
ListNode sortedWholeHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = sortedWholeHead;
ListNode i = sortedList1;
ListNode j = sortedList2;
while(i != null || j != null)
{
if(i == null)
{
ListNode tmp = j;
j = j.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else if(j == null)
{
ListNode tmp = i;
i = i.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else if(i.val > j.val)
{
ListNode tmp = j;
j = j.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else
{
ListNode tmp = i;
i = i.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
}
return sortedWholeHead.next;
}
}
|
2 迭代
参考自https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/solution/148-pai-xu-lian-biao-jiu-yin-wei-zhe-ge-ti-bei-wu-/
这种方法从低到上的进行归并. 就避免了递归
使用cut操作依次把链表分割成长度为size的单元(size从1开始,指数级递增)
使用迭代的方式依次合并分割开的小单元,直到size>=length时,停止循环,返回结果。size表示的即为链表中长度为size的小单元已经是有序的
主要就是cut和merge两个关键操作
cut(curr, n)表示将curr的前n个节点切断, 返回第n+1个节点的指针. 而curr对应的链表就是第1个到第n个的节点.
merge(list1, list2)表示归并两个有序链表, 返回归并后的链表的第一个节点
下面举例说明
链表[5 -1 3 4 0]
首先初始化size = 1, 当前链表curr 为head
我们从当前链表curr中分离出两个长度为size的链表 5 和 -1, 然后归并他们, 变为 -1 -> 5. 将其存储在新的链表中. dummyHead -> -1 -> 5
剩余的链表为3->4->0, 再次分离两个链表, 3, 4. 归并他们 3->4, 然后加到dummyHead最后 dummyHead -> -1 -> 5->3->4
剩余的链表为0, 再次分离两个链表, 0 和 null, 归并他们, 加到dummyHead最后 dummyHead -> -1 -> 5->3->4->0
当再次取两个长度为size的链表的时候, 发现都为空. 跳出这次循环, 更新size = size*2; curr = dummyHead->next.
再次回到步骤 1, 直到size > length
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
|
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
int len = 0;
for(ListNode i = head; i != null; i = i.next)
{
++len;
}
int size = 1;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
while(size < len)
{
ListNode curr = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = null;
ListNode tail = dummyHead;
while(true)
{
ListNode l1 = curr;
curr = cut(curr, size);
ListNode l2 = curr;
curr = cut(curr, size);
if(l1 == null && l2 == null)
break;
ListNode lMerge = merge(l1, l2);
tail.next = lMerge;
while(tail.next != null)
{
tail = tail.next;
}
}
size *= 2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
private ListNode cut(ListNode head, int n)
{
ListNode i = head;
while(n - 1 > 0 && i != null)
{
i = i.next;
--n;
}
if(i == null)
return i;
ListNode res = i.next;
i.next = null;
return res;
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
{
ListNode sortedWholeHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = sortedWholeHead;
ListNode i = list1;
ListNode j = list2;
while(i != null || j != null)
{
if(i == null)
{
ListNode tmp = j;
j = j.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else if(j == null)
{
ListNode tmp = i;
i = i.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else if(i.val > j.val)
{
ListNode tmp = j;
j = j.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
else
{
ListNode tmp = i;
i = i.next;
tmp.next = null;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tail.next;
}
}
return sortedWholeHead.next;
}
}
|

