A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) where random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.
Example 1:
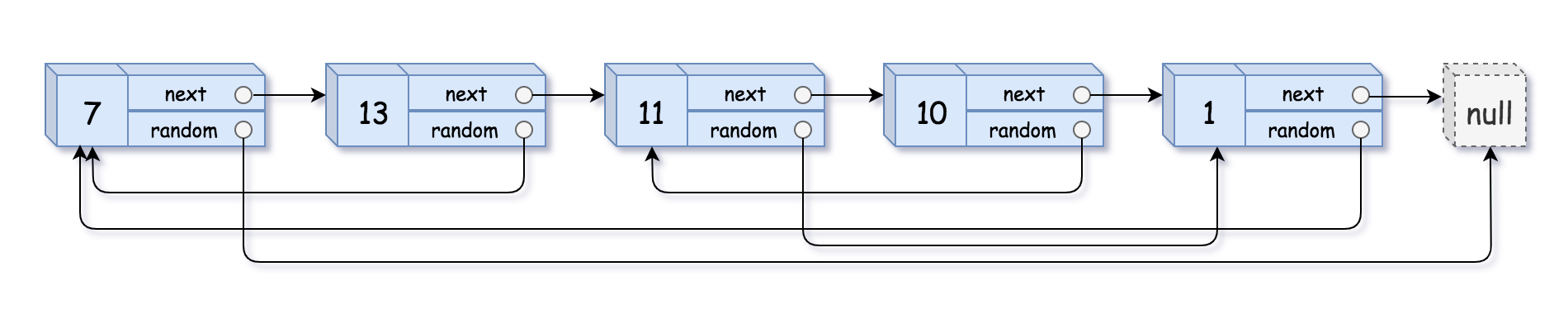
1 2 Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
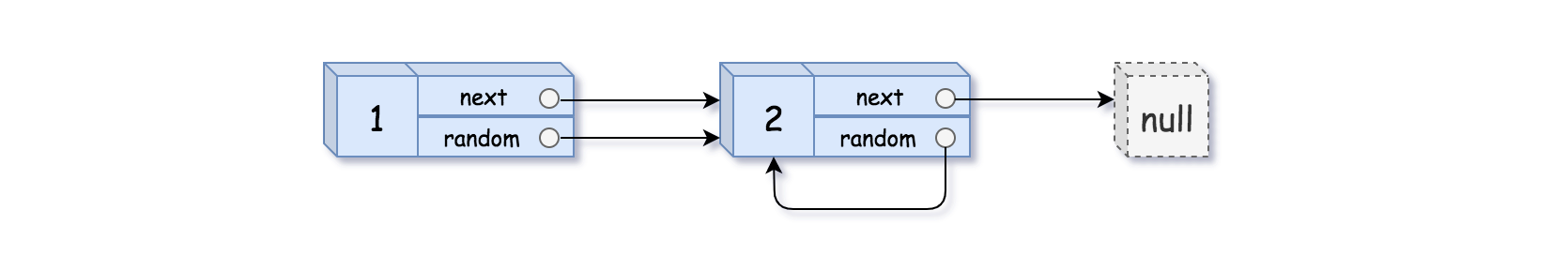
1 2 Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
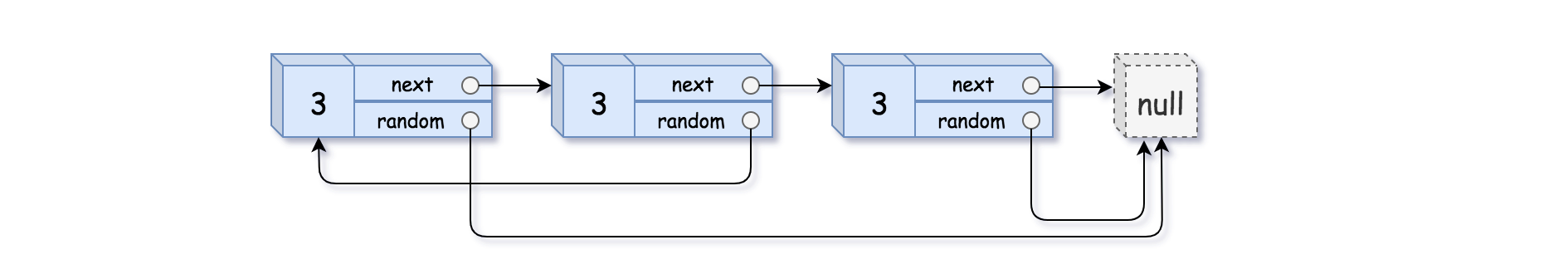
1 2 Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
1 2 3 Input: head = [] Output: [] Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random is null or pointing to a node in the linked list.The number of nodes will not exceed 1000.
1 数组 + hashtable 首先建立一个hashmap<Node, i>, 对应着链表的某个节点在第i个位置上. (从0开始计数)
然后新建一个Node数组, 每个数组都new一个新的Node. 链表遍历一遍, 把链表第i个节点的值复制到数组第i个元素上.
然后数组遍历一遍, 数组第i个元素的next指向数组第i+1个元素.
然后链表遍历一遍, 对于遍历的每一个元素node, 找到这个元素在链表中的位置i, 同时找到node.random在链表中的位置j.
最后在数组中添加nodes[i].random = nodes[j]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution public Node copyRandomList (Node head) if (head == null ) return null ; Map<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); int locationInList = 0 ; for (Node i = head; i != null ; i = i.next) { map.put(i, locationInList); ++locationInList; } int len = locationInList; Node[] nodes = new Node[len]; int k = 0 ; for (Node i = head; i != null ; i = i.next) { nodes[k++] = new Node(i.val); } for (int i = 0 ; i < len - 1 ; ++i) { nodes[i].next = nodes[i+1 ]; } for (Node i = head; i != null ; i = i.next) { int iLocation = map.get(i); if (i.random == null ) nodes[iLocation].random = null ; else { int iRandomLocation = map.get(i.random); nodes[iLocation].random = nodes[iRandomLocation]; } } return nodes[0 ]; } }
2 hashtable 经过1的分析, 发现可以不用那个数组. 直接建立一个原Node到新Node的映射即可.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution public Node copyRandomList (Node head) if (head == null ) return null ; Node newHead = new Node(-1 ); Node tail = newHead; Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); for (Node i = head; i != null ; i = i.next) { Node j = new Node(i.val); map.put(i,j); tail.next = j; tail = tail.next; } Node i = head; Node j = newHead.next; while (i != null ) { Node iRandom = i.random; Node jRandom = map.get(iRandom); j.random = jRandom; i = i.next; j = j.next; } return newHead.next; } }
3 利用链表作为映射 这方法太巧妙了(日常感叹答案的巧妙哈哈哈).
对于原链表a->b->c, 我们仍然需要原链表某一个节点到对应链表的节点的映射.
这时, 把新链表的那个节点都插入到原链表对应节点的后面, 变成a->a'->b->b'->c->c'
这样不需要hashtable也能存储原来的映射了!!!
首先要重新赋值新链表的random指针,
如果原链表的random指针为a.ramdom == c, 那么根据我们的映射, 就能得到a.next.random == c.next!
然后再将两条链表分离出来即可.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution public Node copyRandomList (Node head) if (head == null ) return null ; for (Node i = head; i != null ;) { Node tmp = i.next; Node i_ = new Node(i.val); i.next = i_; i_.next = tmp; i = tmp; } for (Node i = head; i != null ;) { Node iRandom = i.random; i.next.random = (iRandom == null ) ? null : iRandom.next; i = i.next.next; } Node newHead = head.next; Node j = newHead; for (Node i = head; i != null ;) { i.next = i.next.next; j.next = j.next == null ? null : j.next.next; i = i.next; j = j.next; } return newHead; } }